VRF (Randomness) in Solidity
Introduction
Flow provides secure, native on-chain randomness that developers can leverage through Cadence Arch, a precompiled contract available on the Flow EVM environment. This guide will walk through how Solidity developers can use Cadence Arch to access Flow’s verifiable randomness using Solidity.
What is Cadence Arch?
Cadence Arch is a precompiled smart contract that allows Solidity developers on Flow EVM to interact with Flow’s randomness and other network features like block height. This contract can be accessed using its specific address, and Solidity developers can make static calls to retrieve random values and other information.
Prerequisites
- Basic Solidity knowledge.
- Installed Metamask extension.
- Remix IDE for compilation and deployment.
- Flow EVM Testnet setup in Metamask.
Network Information for Flow EVM
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Network Name | EVM on Flow Testnet |
| RPC Endpoint | https://testnet.evm.nodes.onflow.org |
| Chain ID | 545 |
| Currency Symbol | FLOW |
| Block Explorer | https://evm-testnet.flowscan.io |
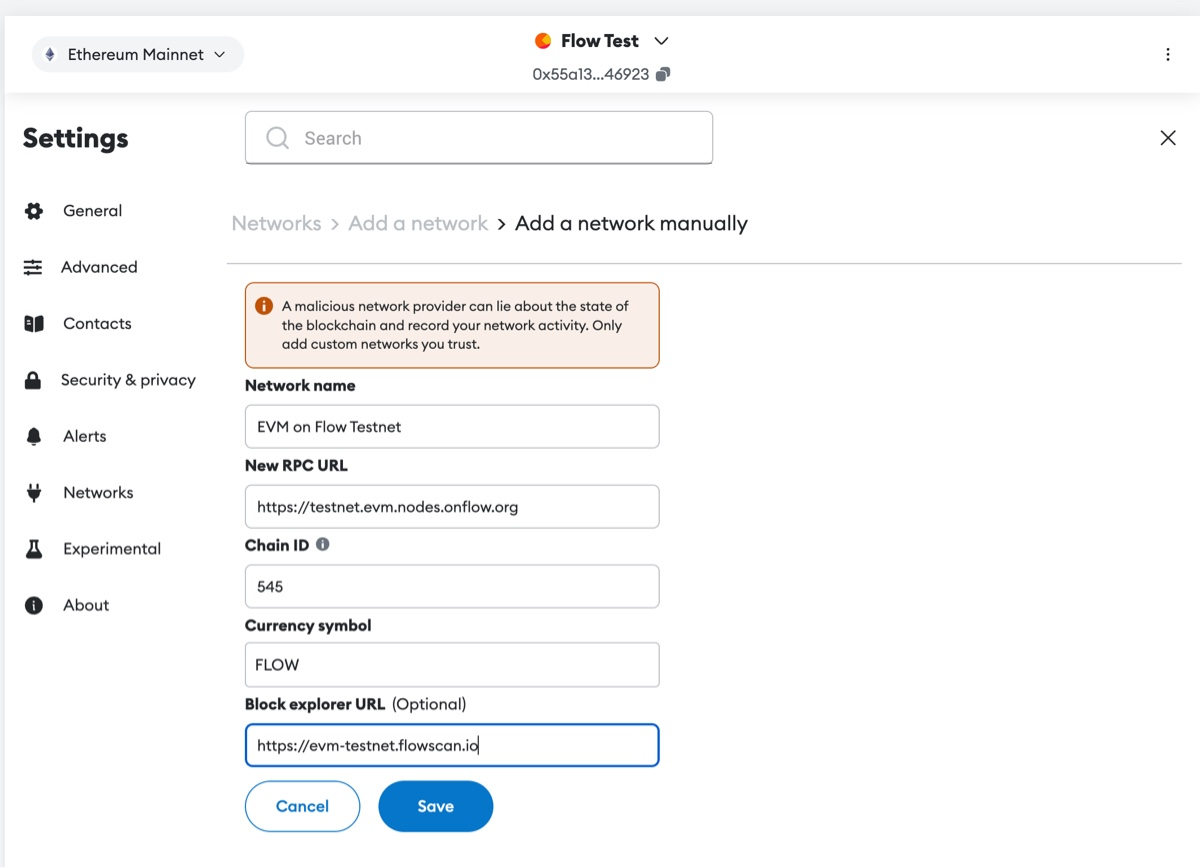
Steps to Connect Flow EVM Testnet to Metamask
- Open Metamask and click Networks -> Add Network.
- Enter the following details:
- Network Name: EVM on Flow Testnet
- RPC URL:
https://testnet.evm.nodes.onflow.org - Chain ID:
545 - Currency Symbol:
FLOW - Block Explorer:
https://evm-testnet.flowscan.io
- Click Save and switch to the Flow EVM Testnet.
Obtaining Testnet FLOW
You can fund your account with testnet FLOW using the Flow Faucet. Enter your Flow-EVM testnet address, and you’ll receive testnet FLOW tokens to interact with smart contracts.
Solidity Code Example: Retrieving Random Numbers
Below is a simple Solidity contract that interacts with the Cadence Arch contract to retrieve a pseudo-random number.
_17// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0_17pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;_17_17contract CadenceArchCaller {_17 // Address of the Cadence Arch contract_17 address constant public cadenceArch = 0x0000000000000000000000010000000000000001;_17_17 // Function to fetch a pseudo-random value_17 function revertibleRandom() public view returns (uint64) {_17 // Static call to the Cadence Arch contract's revertibleRandom function_17 (bool ok, bytes memory data) = cadenceArch.staticcall(abi.encodeWithSignature("revertibleRandom()"));_17 require(ok, "Failed to fetch a random number through Cadence Arch");_17 uint64 output = abi.decode(data, (uint64));_17 // Return the random value_17 return output;_17 }_17}
Explanation of the Contract
-
Cadence Arch Address:
The
cadenceArchvariable stores the address of the Cadence Arch precompiled contract (0x0000000000000000000000010000000000000001), which is constant across Flow EVM. -
Revertible Random:
The
revertibleRandom()function makes a static call to therevertibleRandom<uint64>()function to fetch a pseudo-random number. If the call is successful, it decodes the result as auint64random value.
Deploying and Testing the Contract
Compile and Deploy the Contract
- Open Remix IDE.
- Create a new file and paste the Solidity code above.
- Compile the contract by selecting the appropriate Solidity compiler version (0.8.x).
- Connect Remix to your Metamask wallet (with Flow EVM testnet) by selecting Injected Web3 as the environment.
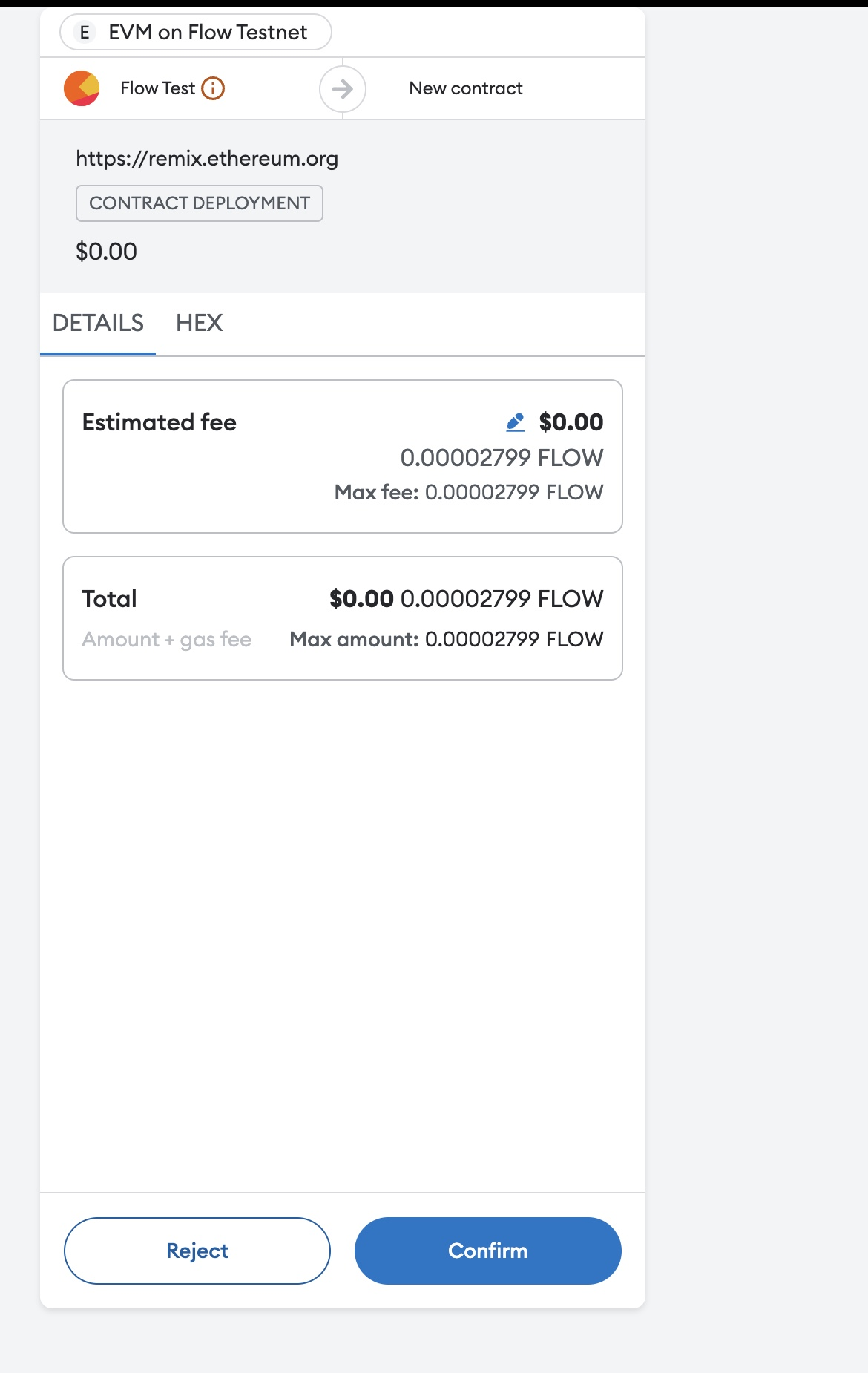
- Deploy the contract.
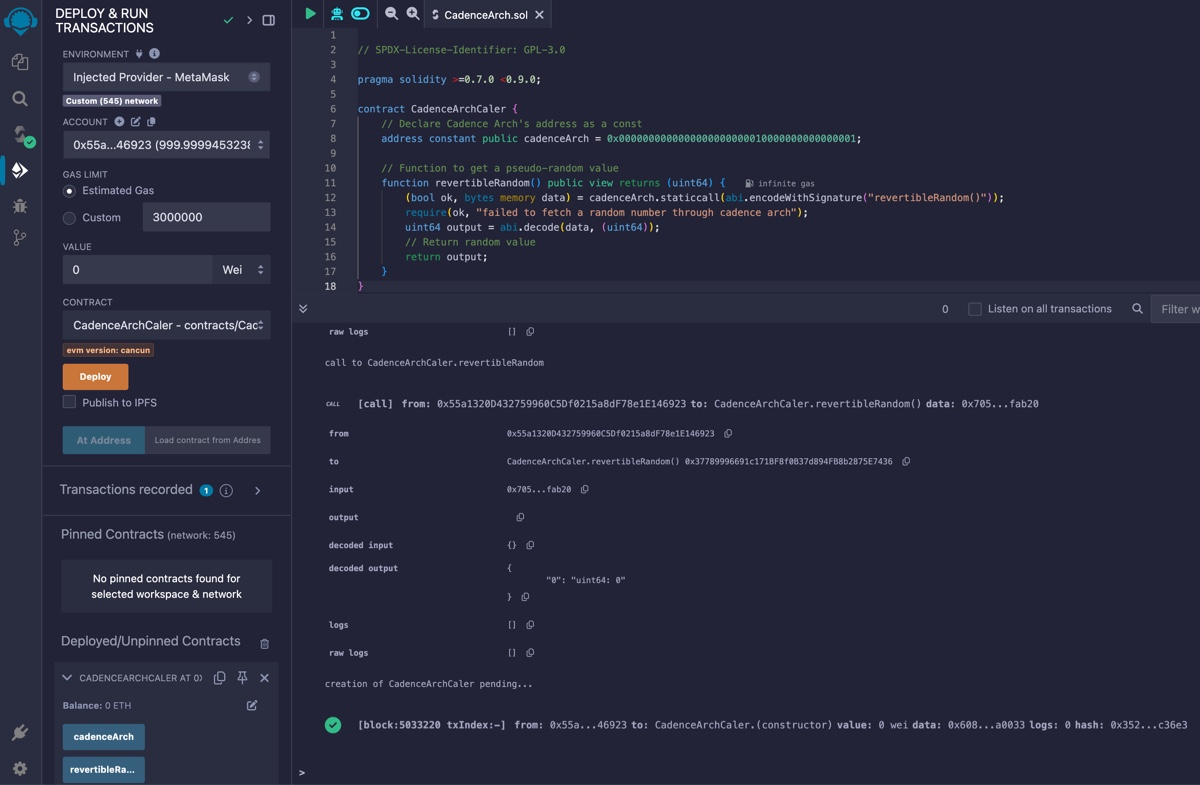
Call revertibleRandom
After deployment, you can interact with the contract to retrieve a random number.
Call the revertibleRandom() function in the left sidebar on the deployed contract. This will fetch a pseudo-random
number generated by Flow’s VRF.
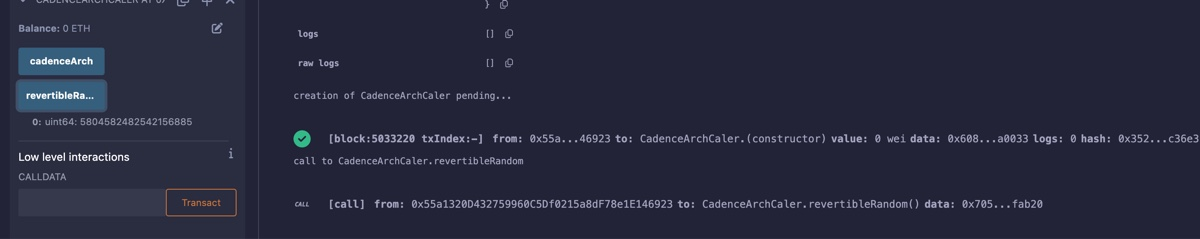
The result will be a uint64 random number generated on Flow EVM.
Generating Random Numbers in a Range
For use-cases like games and lotteries, it’s useful to generate a random number within a specified range, the following example shows how to get a value between a min and max number.
_17// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0_17pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;_17_17contract RandomInRange {_17 address constant public cadenceArch = 0x0000000000000000000000010000000000000001;_17_17 // Generate a random number between min and max_17 function getRandomInRange(uint64 min, uint64 max) public view returns (uint64) {_17 // Static call to the Cadence Arch contract's revertibleRandom function_17 (bool ok, bytes memory data) = cadenceArch.staticcall(abi.encodeWithSignature("revertibleRandom()"));_17 require(ok, "Failed to fetch a random number through Cadence Arch");_17 uint64 randomNumber = abi.decode(data, (uint64));_17_17 // Return the number in the specified range_17 return (randomNumber % (max + 1 - min)) + min;_17 }_17}
:::warningThe above code is susceptible to the [modulo] bias, particularly if the random number range is not a multiple of your desired range. To avoid this, you can use a more complex algorithm like rejection sampling, an example for which is provided in this repository. :::
Secure Randomness with Commit-Reveal Scheme in Solidity
The revertibleRandom() function can be directly used to generate a pseudo-random number. However, in certain
situations, especially involving untrusted callers, this function exposes a vulnerability: the ability of a transaction
to revert after seeing the random result.
The Issue with Using revertibleRandom() Directly:
- When an untrusted party calls a contract function that uses
revertibleRandom(), they receive the random number during the transaction execution. - Post-selection is the ability of the caller to abort the transaction if the random outcome is unfavorable. In this case, the user could choose to revert the transaction (for example, if they lose a bet) and attempt to call the function again in hopes of a better outcome.
- This can lead to a form of transaction reversion attack, where the randomness can be exploited by repeatedly attempting transactions until a favorable result is obtained.
Read More
For further details on Flow’s randomness and secure development practices, check out the Flow Randomness Documentation.
You can also view an example in both Solidity and Cadence of a random coin toss implentation using the VRF.
This documentation was contributed by Noah Naizir, a community developer.